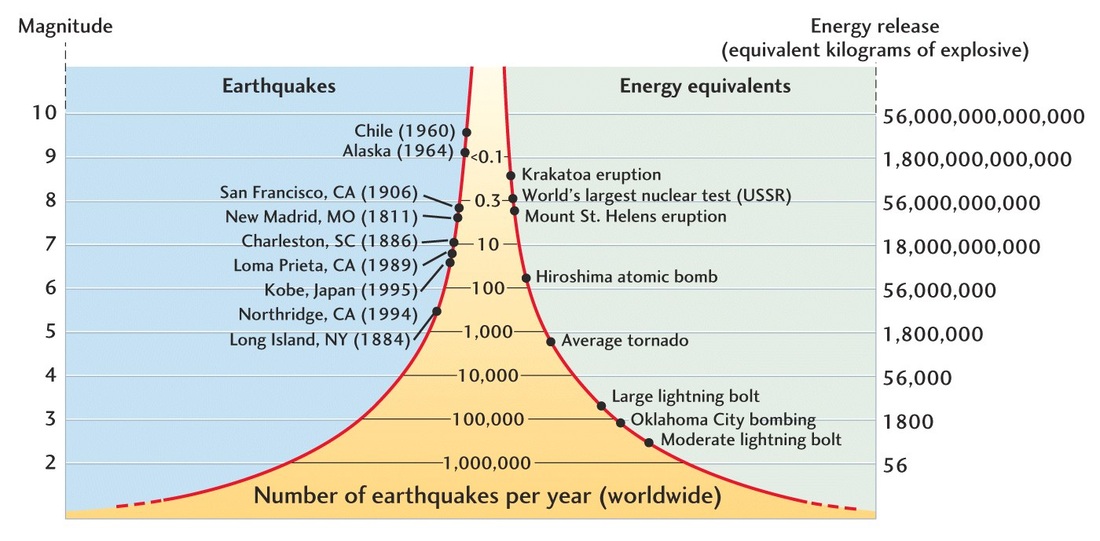
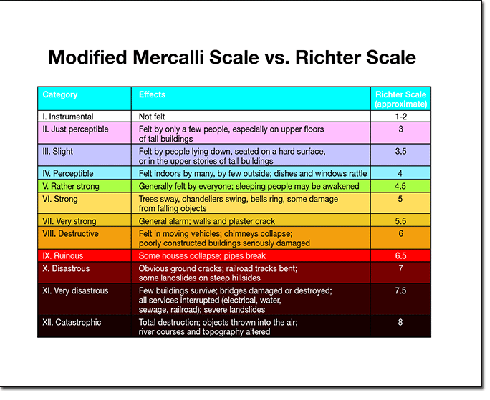
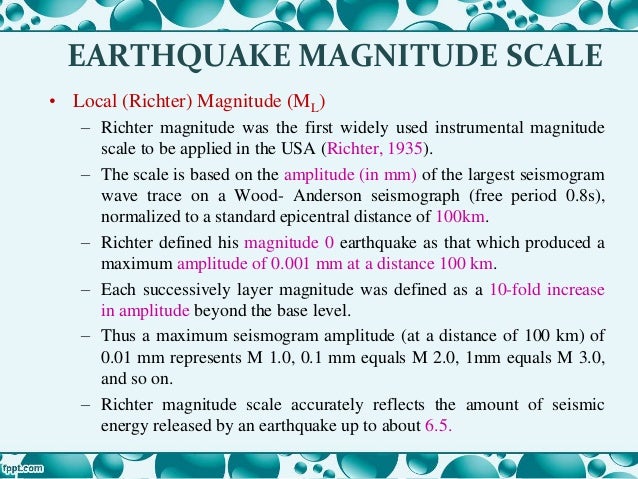
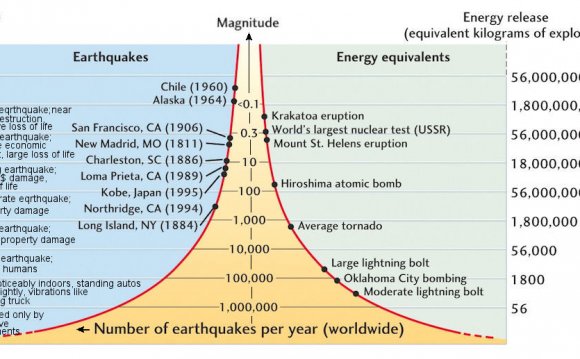
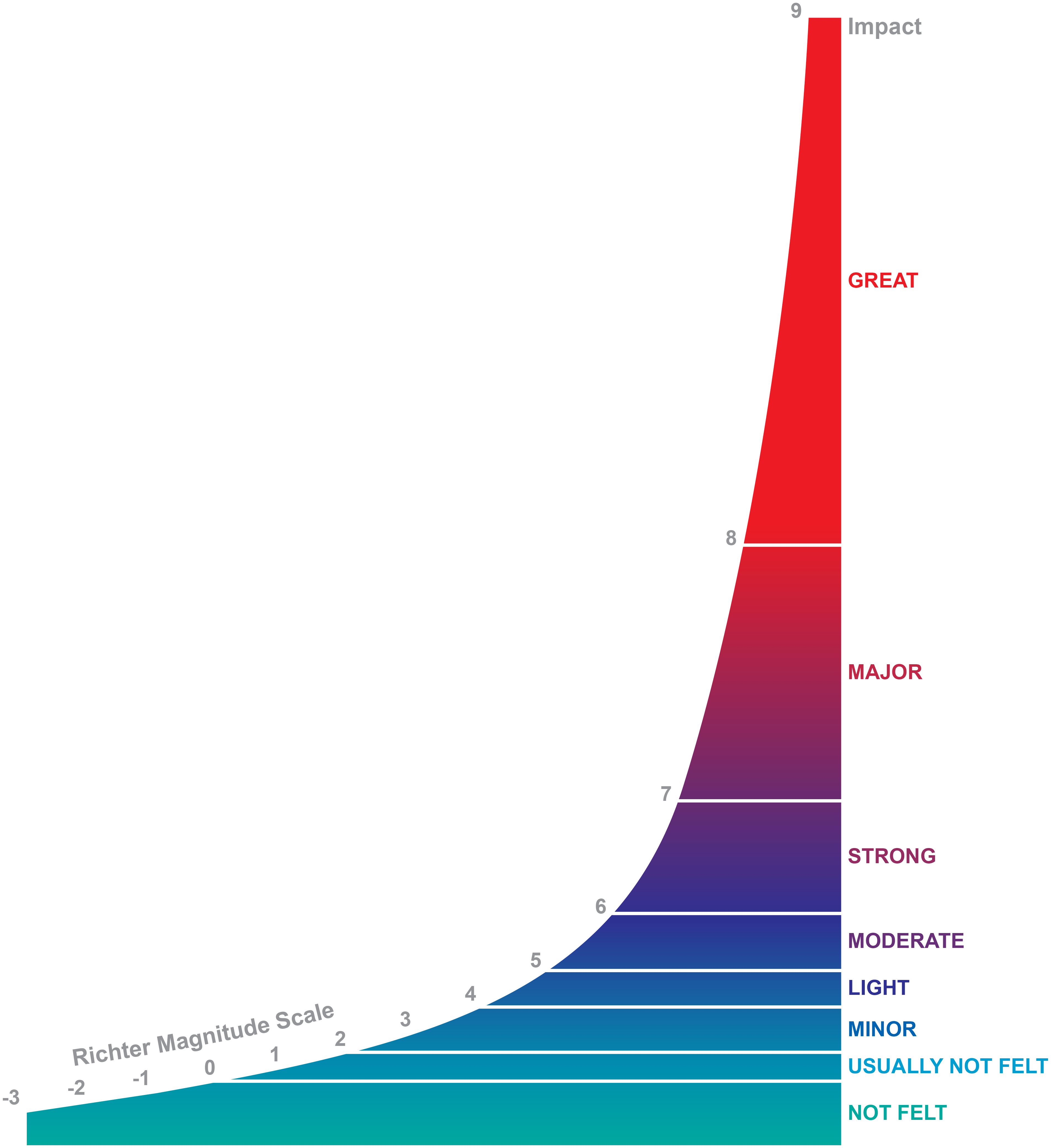
Earthquake Scale Meaning

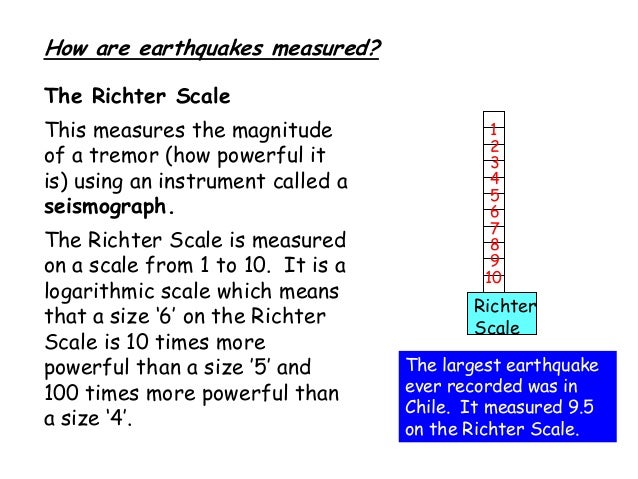
The idea of a logarithmic earthquake magnitude scale was first developed by charles richter in the 1930 s for measuring the size of earthquakes occurring in southern california using relatively high frequency data from nearby seismograph stations.
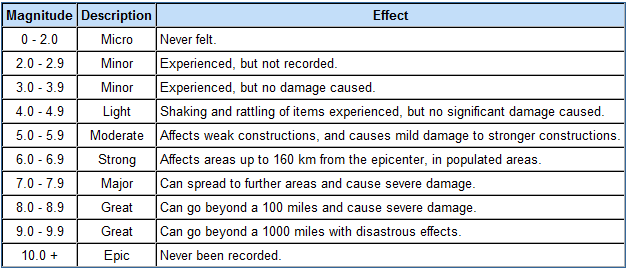
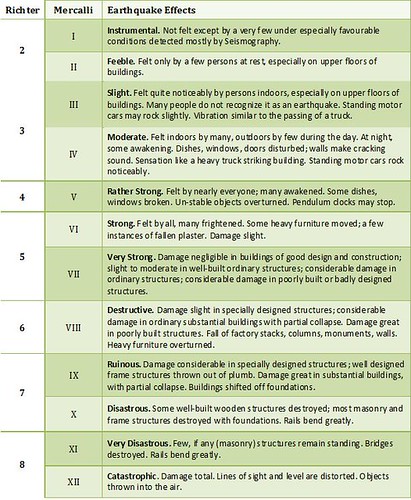
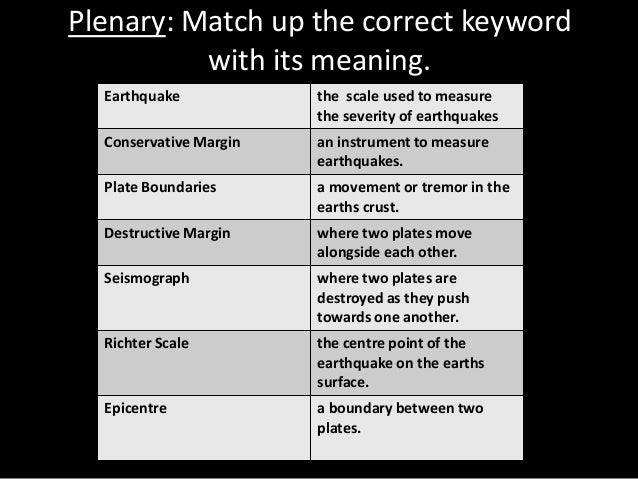
Earthquake scale meaning. Magnitude is based on measurement of the maximum motion recorded by a seismograph several scales have been defined but the most commonly used are 1 local magnitude ml commonly referred to as richter magnitude 2 surface wave magnitude ms 3 body wave magnitude mb and 4 moment. Magnitudes are usually determined from measurements of an earthquake s seismic waves as recorded on a seismogram. Richter scale widely used quantitative measure of an earthquake s magnitude size devised in 1935 by american seismologists charles f.
Learn more about the causes and effects of earthquakes in this article. The richter scale also called the richter magnitude scale or richter s magnitude scale is a measure of the strength of earthquakes developed by charles f. Earthquake any sudden shaking of the ground caused by the passage of seismic waves through earth s rocks.
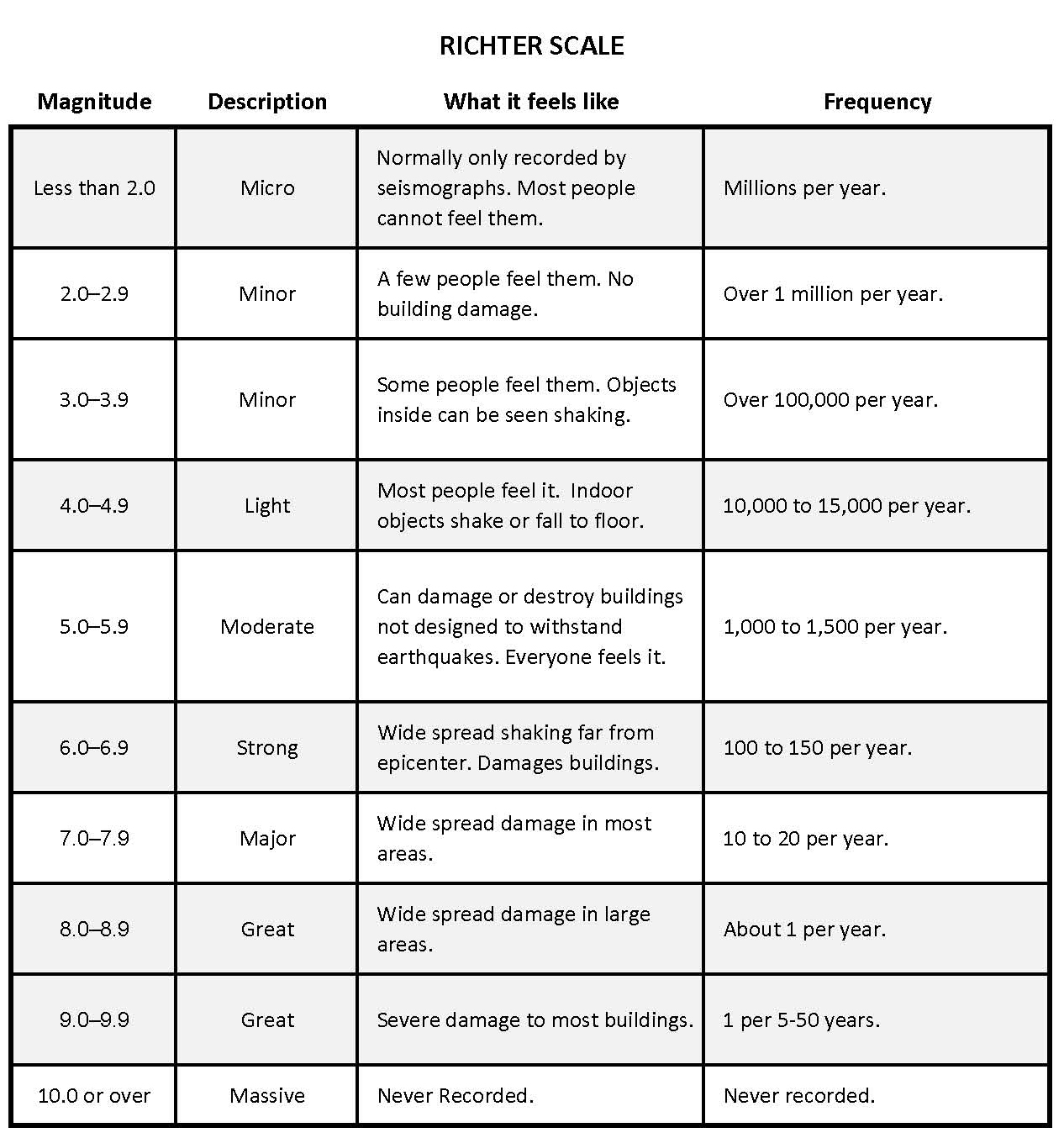
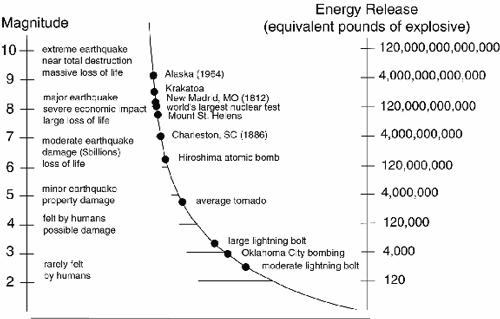
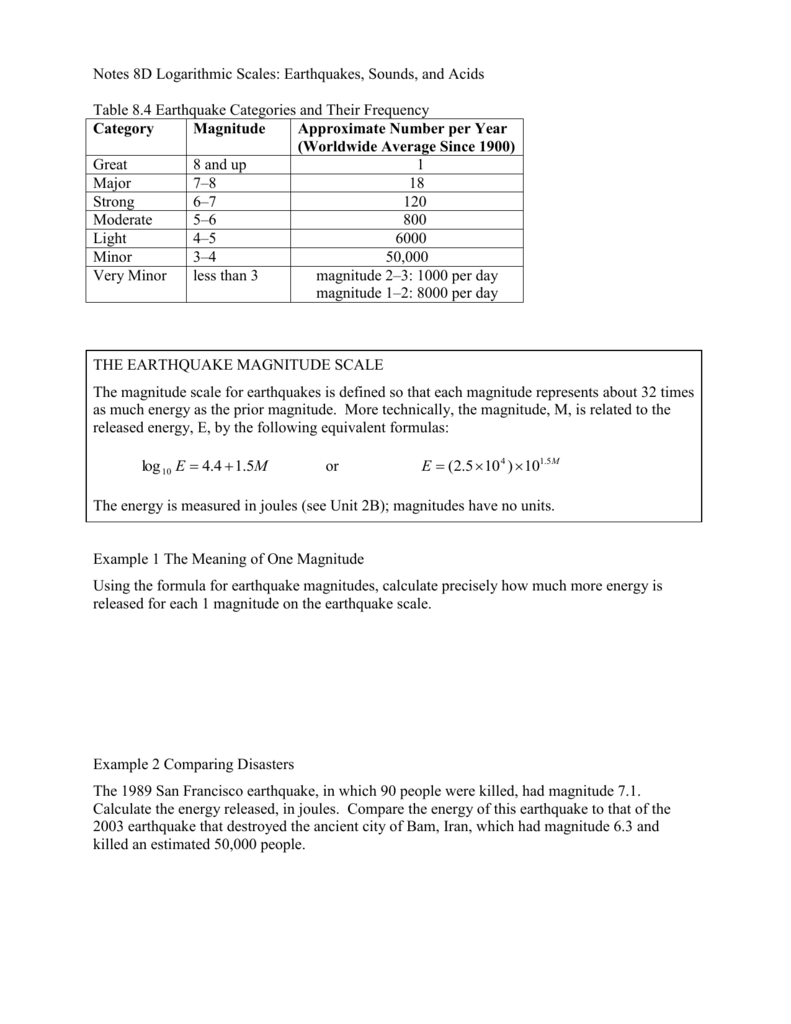
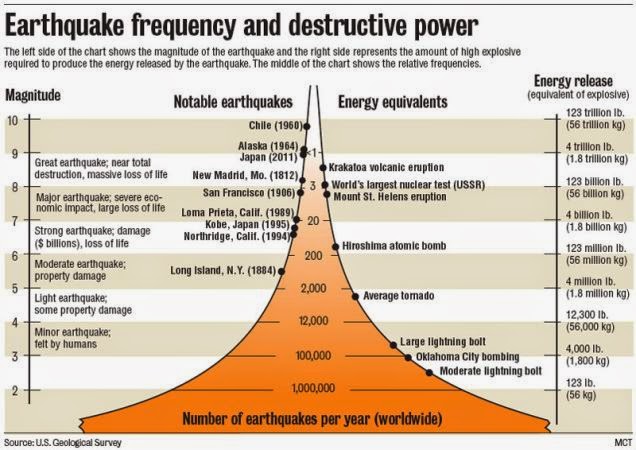
Estimated number each year. Richter scale definition a scale ranging from 1 to 10 for indicating the intensity of an earthquake. Richter and beno gutenberg.
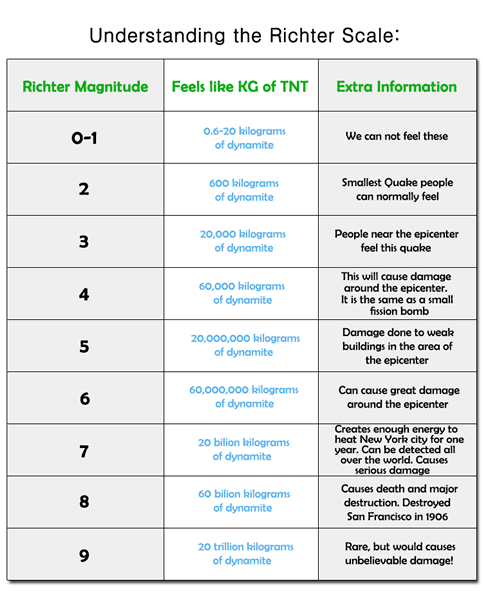
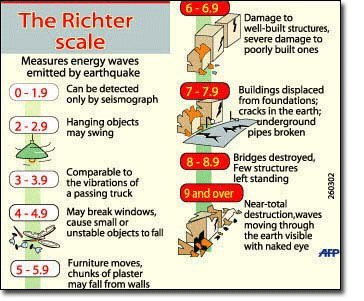
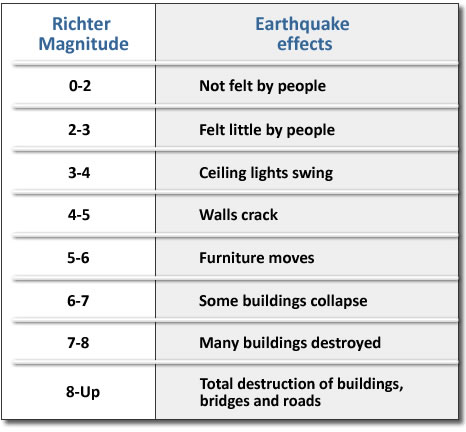
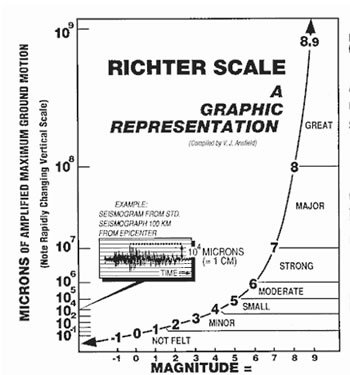
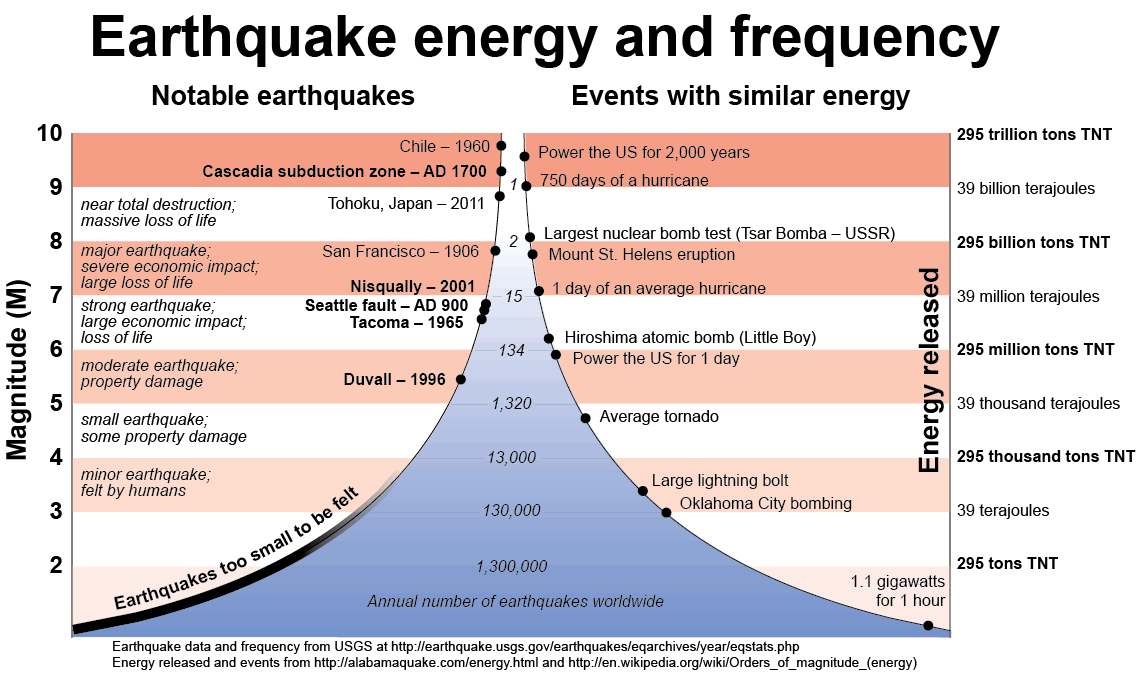
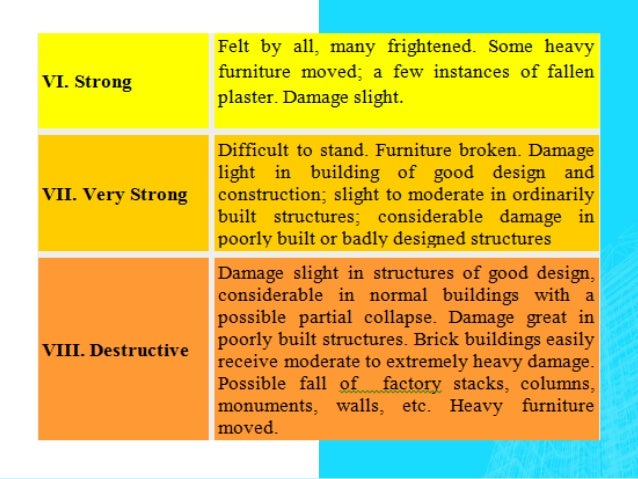
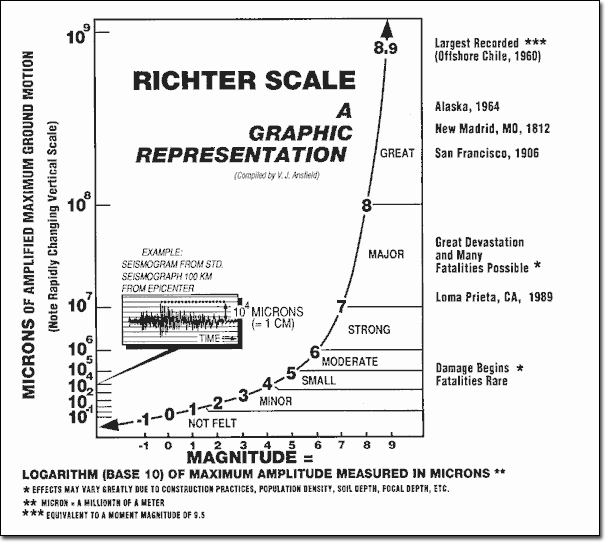
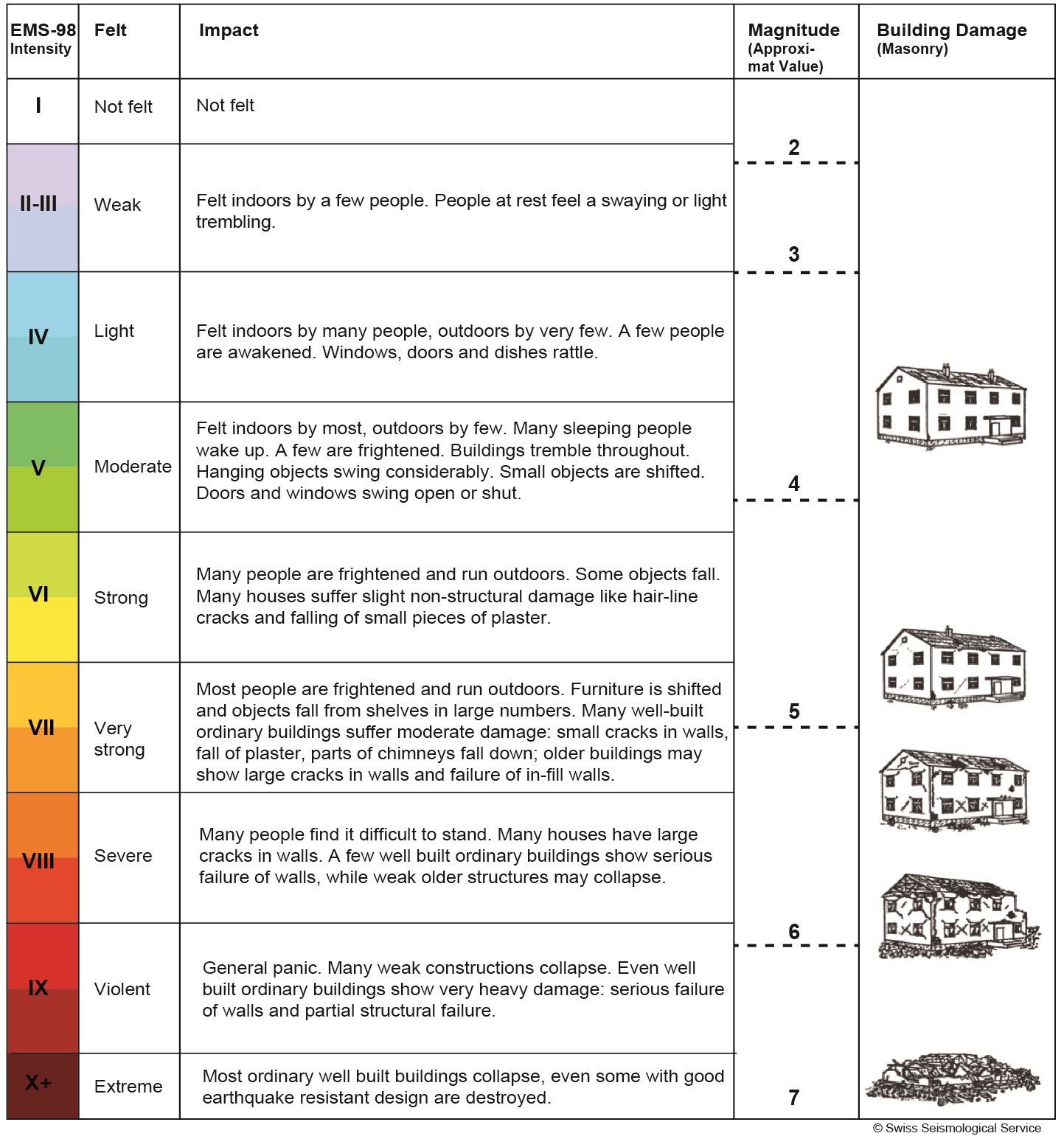
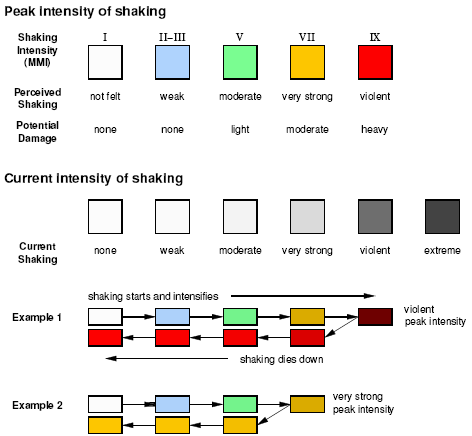
The richter scale runs from 1 to 10 with 1 being the smallest and 10 being the largest. Usually not felt but can be recorded by seismograph. Seismic magnitude scales are used to describe the overall strength or size of an earthquake these are distinguished from seismic intensity scales that categorize the intensity or severity of ground shaking quaking caused by an earthquake at a given location.
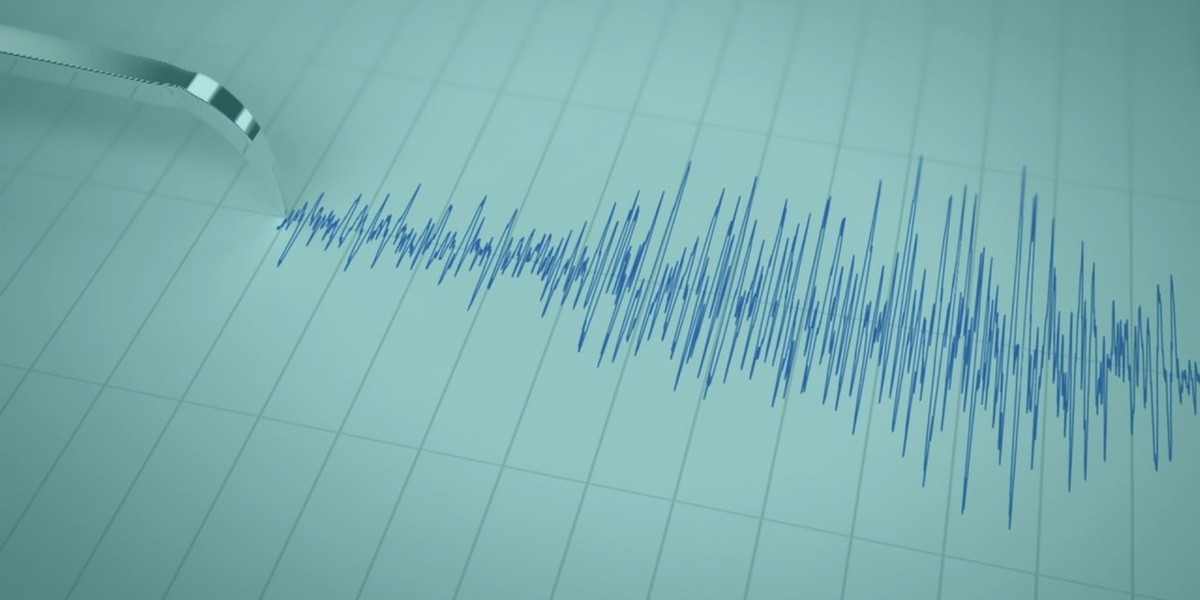
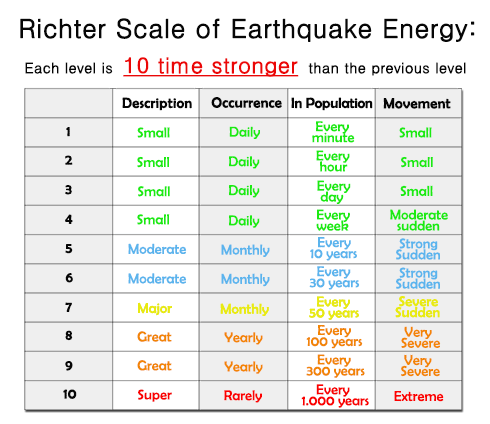
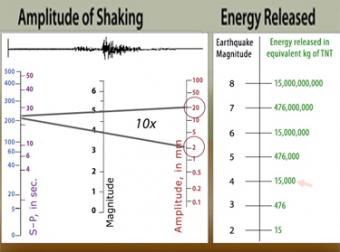
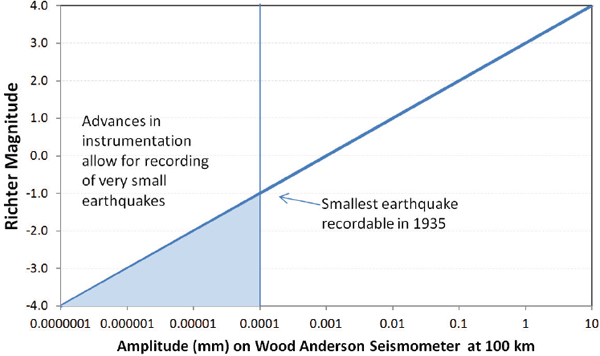
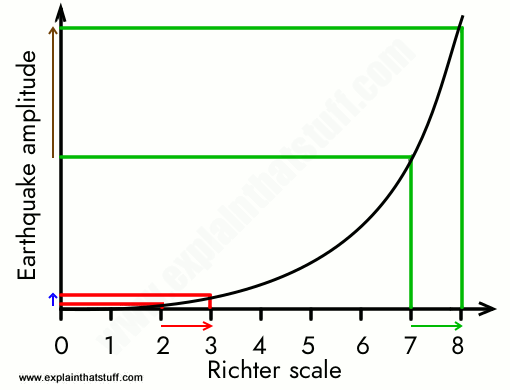
The richter scale is a base 10 logarithmic scale meaning that there is no limit to how small or large the earthquake must be to be measured by the scale. Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 paper where he called it the magnitude scale. The magnitude is a number that characterizes the relative size of an earthquake.
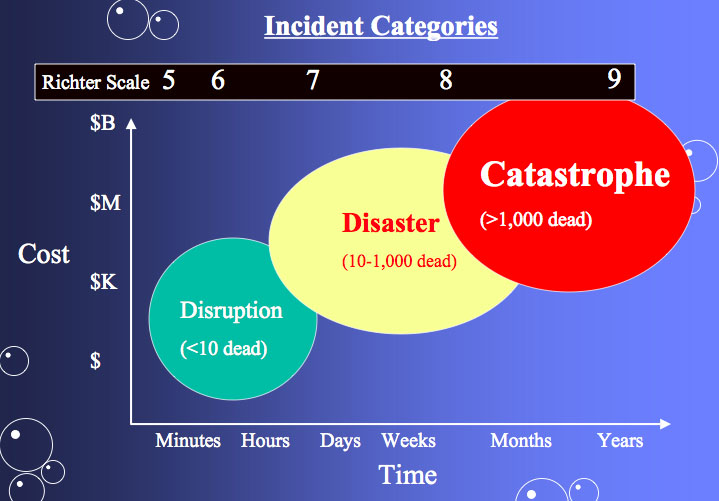
Often felt but. An earthquake also known as a quake tremor or temblor is the shaking of the surface of the earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the earth s lithosphere that creates seismic waves earthquakes can range in size from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air and wreak destruction across entire cities. Earthquake size as measured by the richter scale is a well known but not well understood concept.
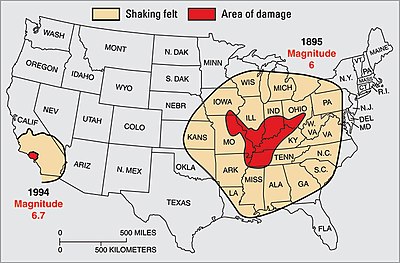
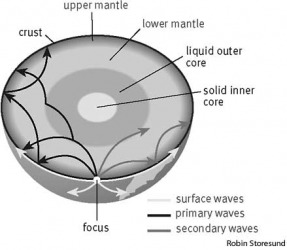
Earthquakes occur most often along geologic faults narrow zones where rock masses move in relation to one another.