Earthquake Magnitudes Explained

Because of various shortcomings of the m l scale most.
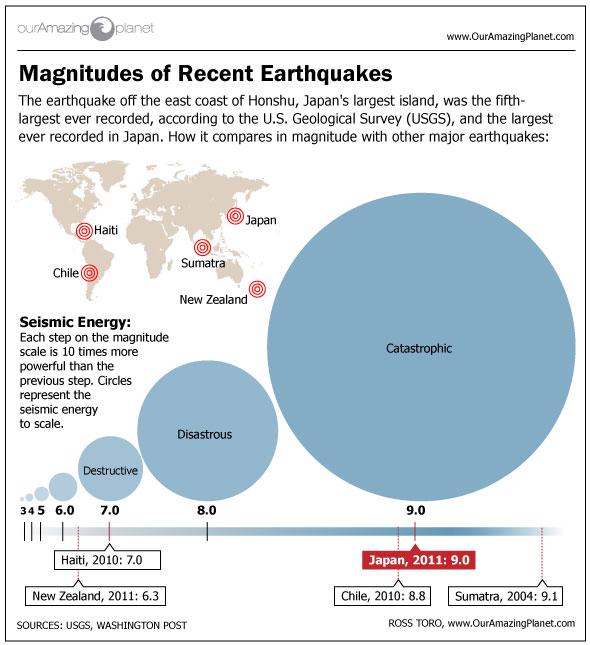
Earthquake magnitudes explained. Usually not felt but can be recorded by seismograph. By robert coontz mar. A massive magnitude 8 8 earthquake struck near the coast of south central chile in the early hours of saturday shaking buildings in the capital santiago 320km away and triggering a tsunami along.
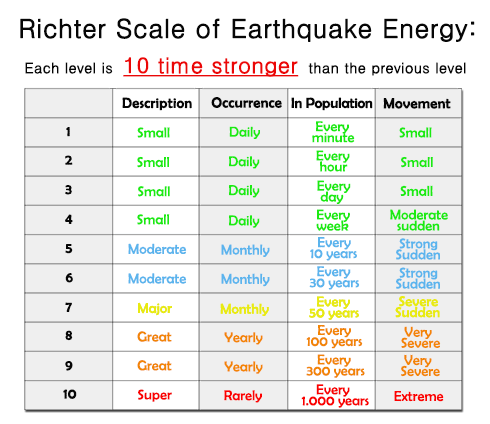
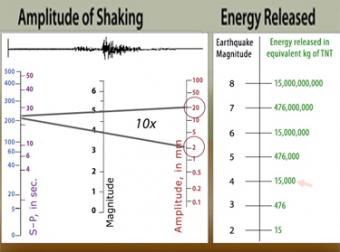
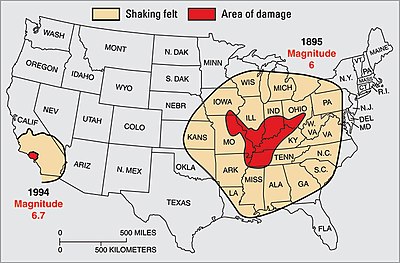
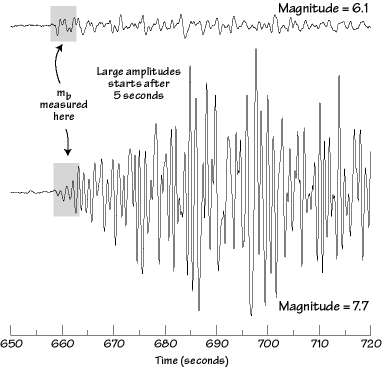
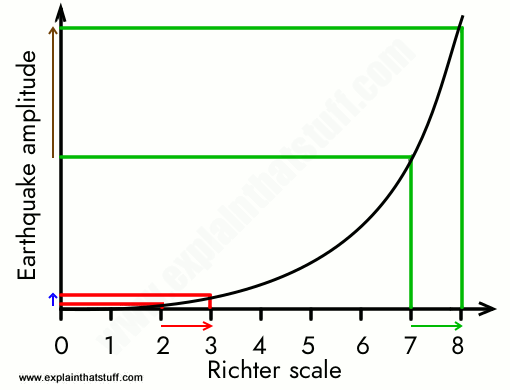
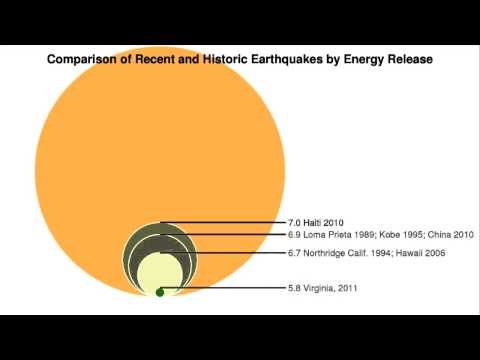
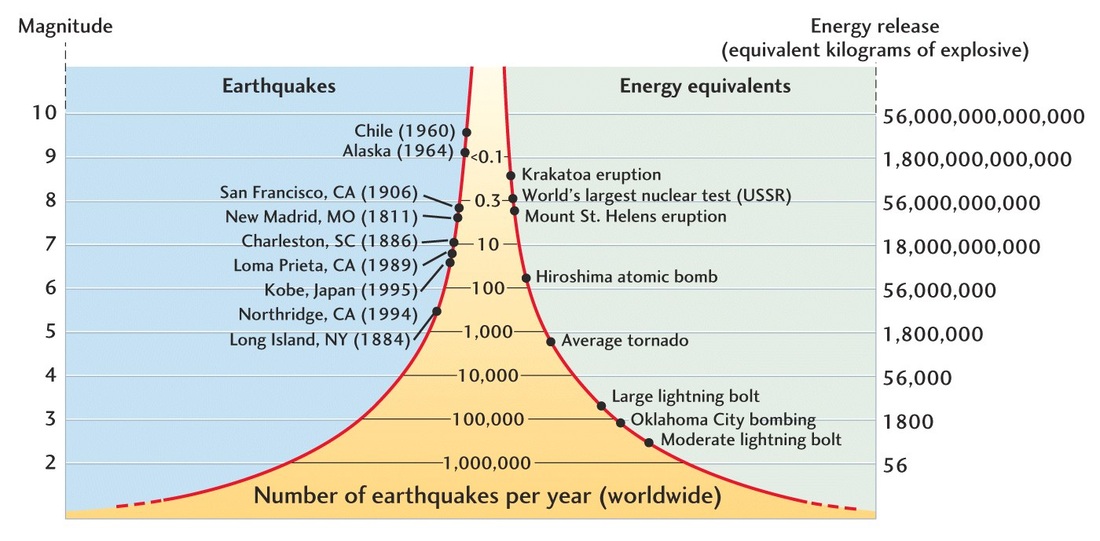
Than the difference in magnitudes is 2 so the stronger earthquake shakes 10 2 or 100 times as hard as the milder one. Video on earthquake magnitudes moment magnitude explained. Estimated number each year.
The types and nature of these waves are described in the section seismic waves because the size of earthquakes varies enormously it is necessary for purposes of comparison to compress the range of wave amplitudes. Looking at earthquake history. This was later revised and renamed the local magnitude scale denoted as ml or m l.
Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 paper where he called it the magnitude scale. But prior to seismographs magnitudes have to be estimated. Seismographs started being used in around 1890 and as a result for earthquakes between 1890 and 1935 when the richter scale was introduced scientists can go back to the historical seismograph records and determine the richter scale.
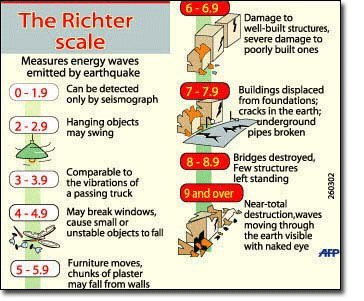
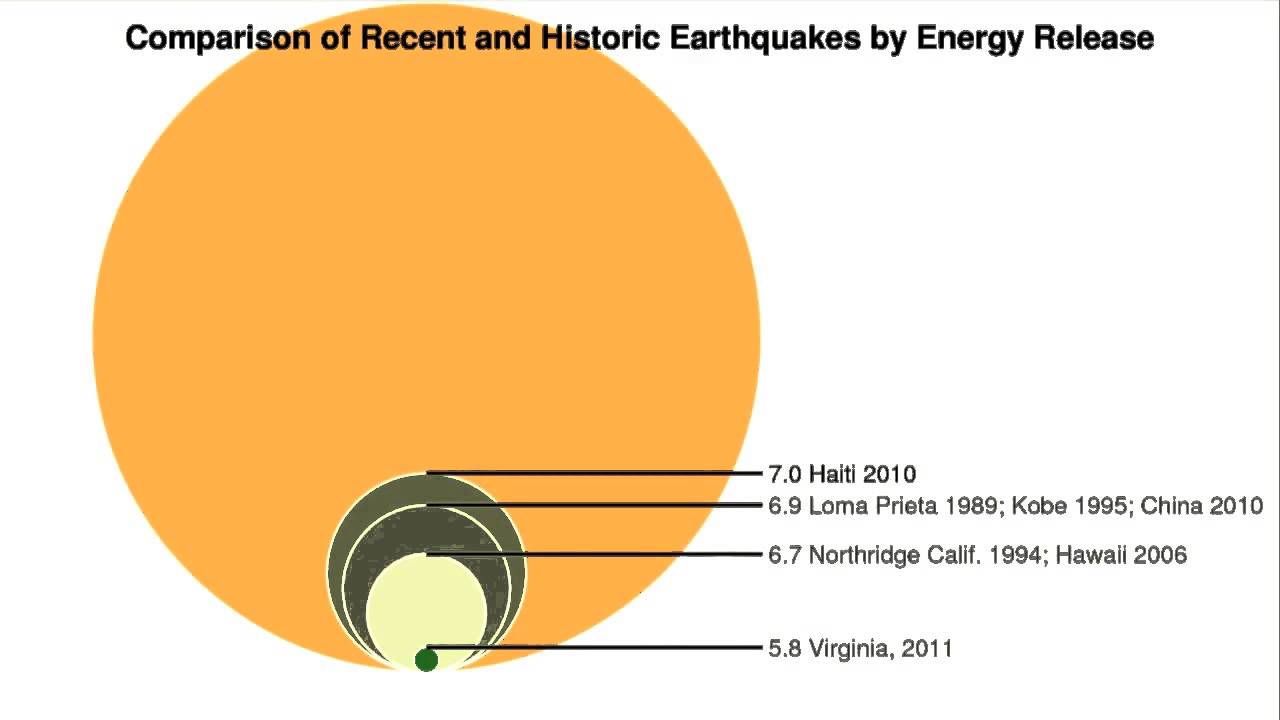
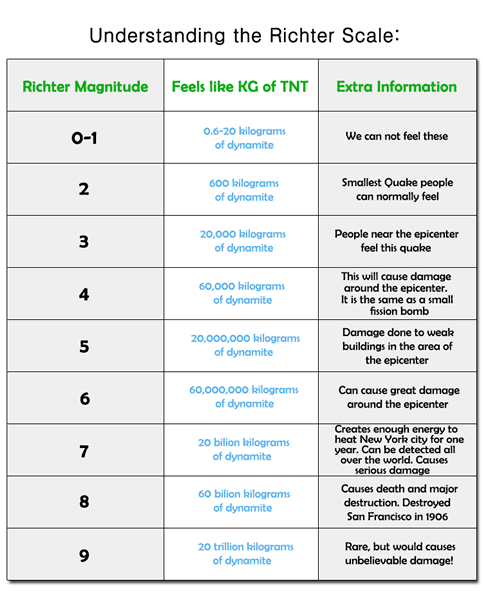
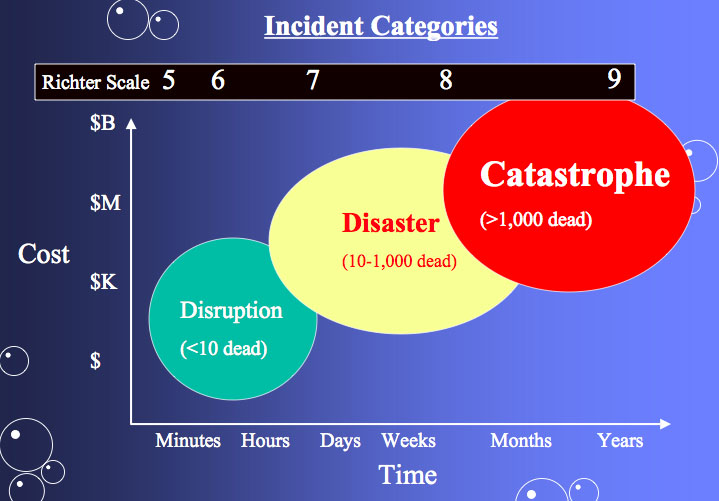
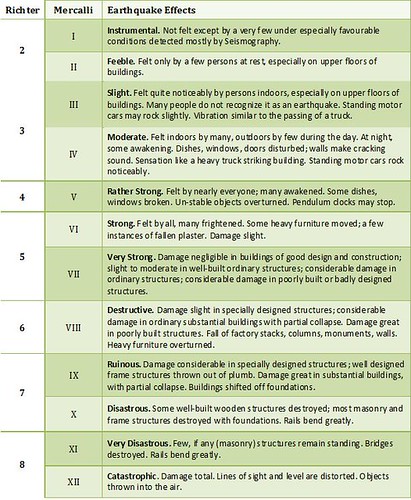
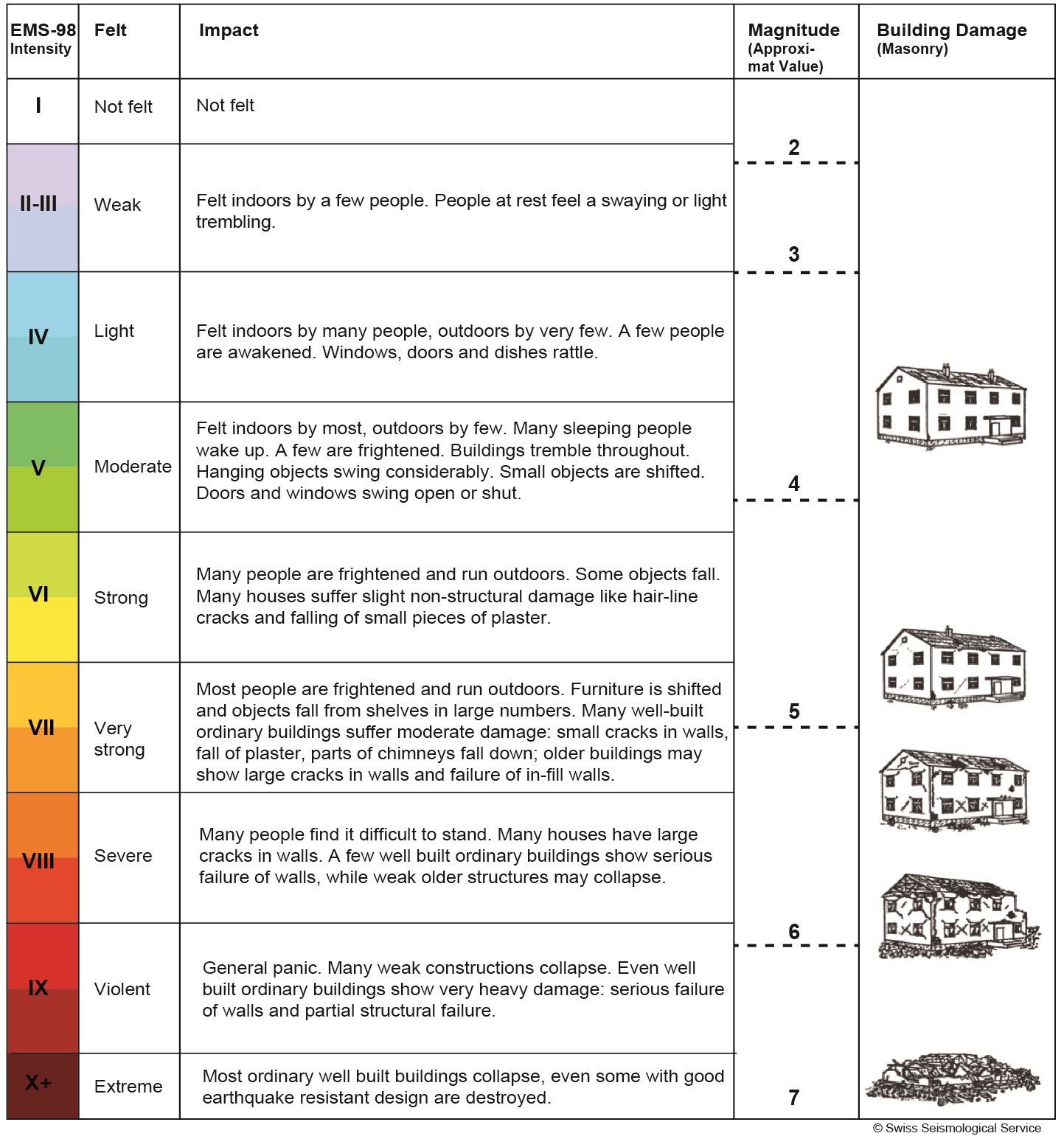
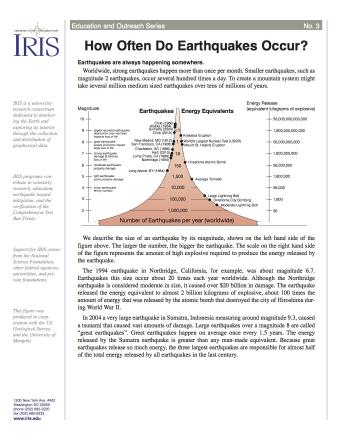
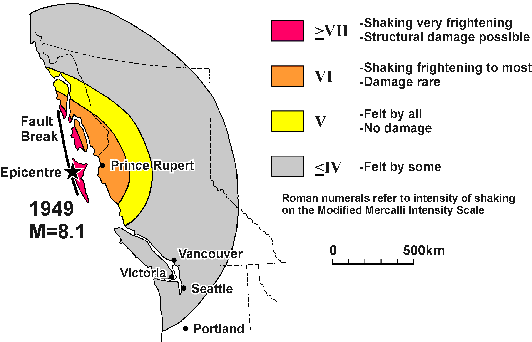
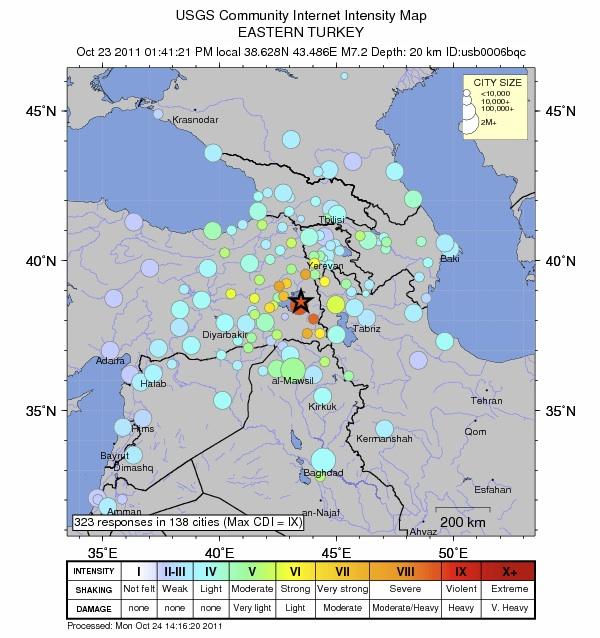
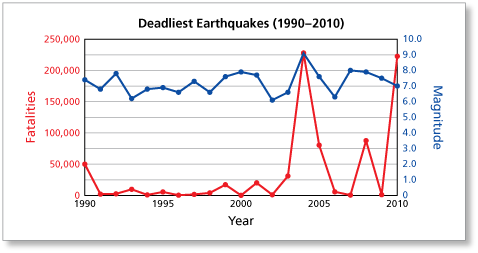
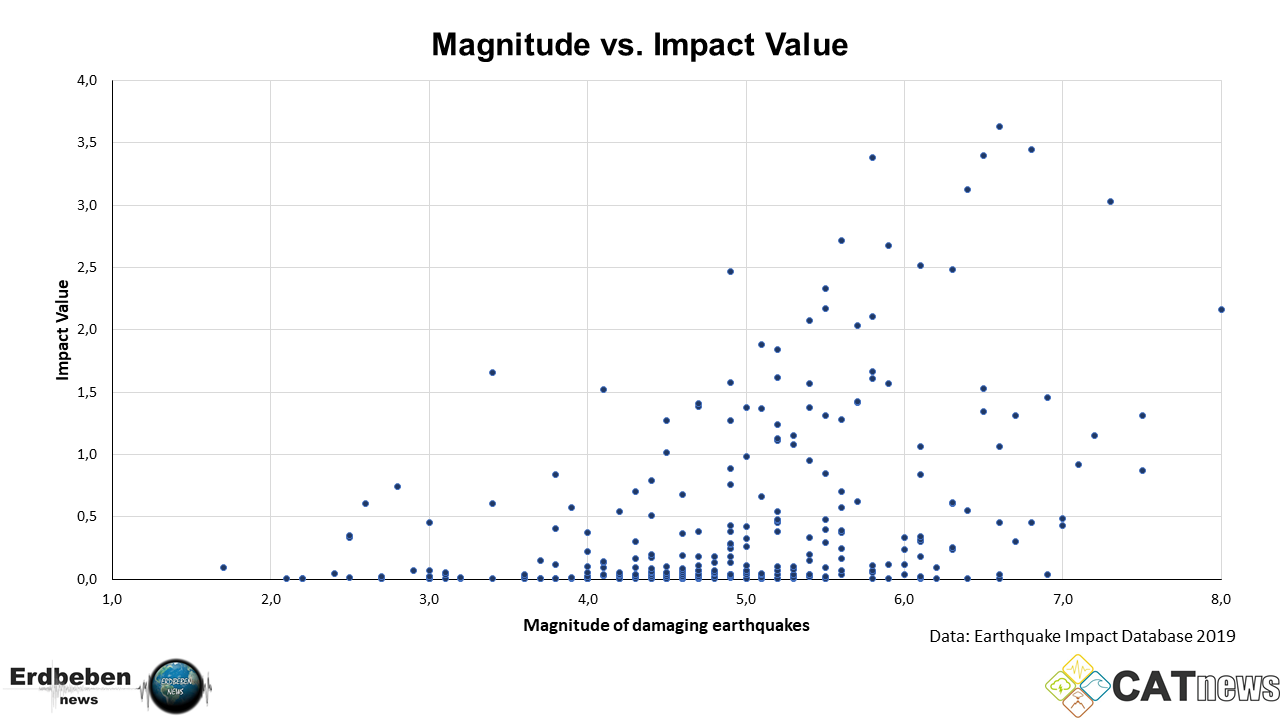
Originally earthquake magnitudes were based on the amplitude of ground motion displacement as measured by a standard seismograph. Magnitude measures the energy released at the earthquake s source while intensity measures the strength of shaking. This fact sheet illustrates information on the frequency of earthquakes of various magnitudes along with details on the effects of earthquakes and the equivalent energy release.
Often felt but. Earthquakes with very large magnitudes and occurring deep beneath the oceanic crust deep focus earthquakes might not be even felt by us on the surface regions. The best known of these is the richter magnitude which was defined for local earthquakes in southern california.
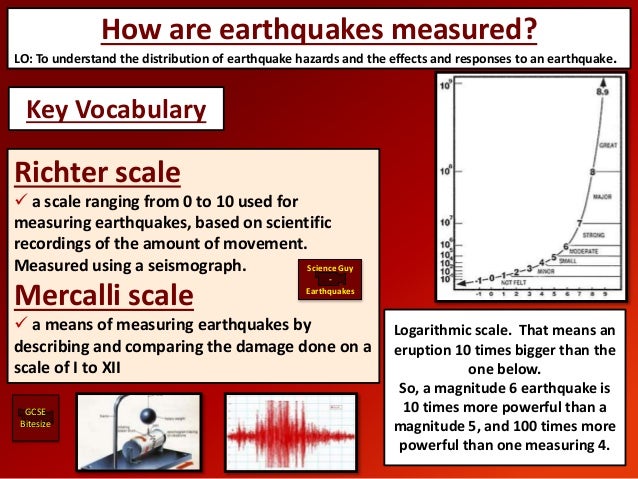
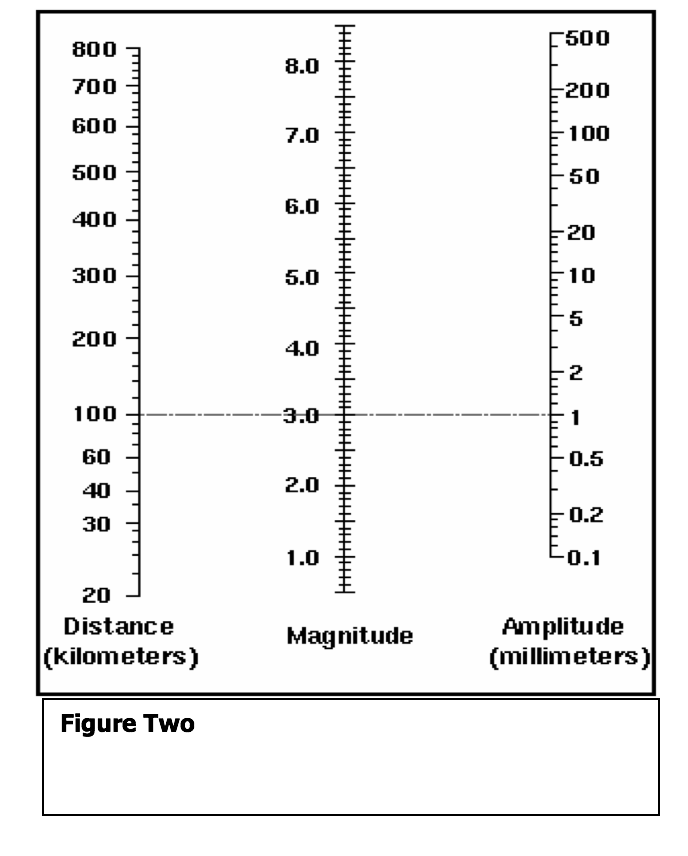
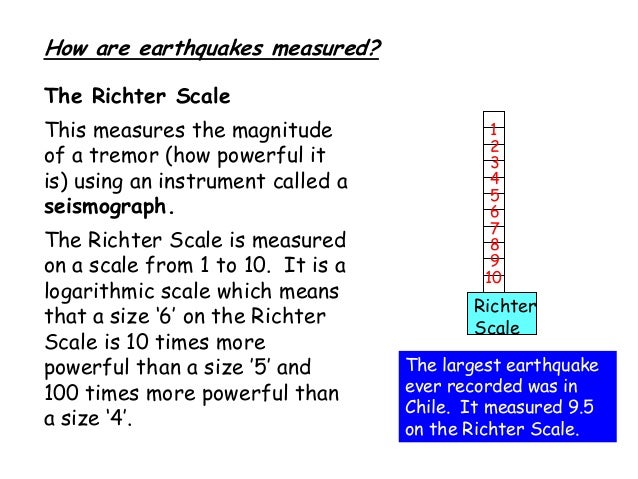
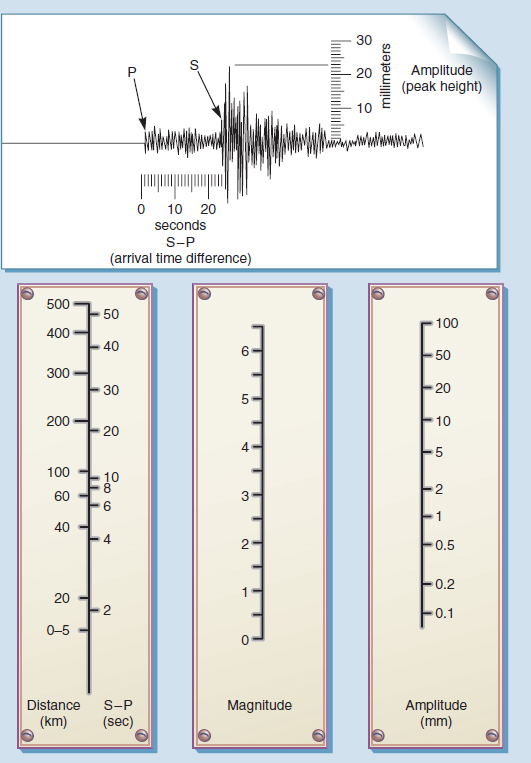
Earthquake magnitude is a measure of the size or amplitude of the seismic waves generated by an earthquake source and recorded by seismographs. The richter scale also called the richter magnitude scale or richter s magnitude scale is a measure of the strength of earthquakes developed by charles f.